RKE2 Networking Guide
This guide covers the networking architecture, configuration, and best practices for production RKE2 deployments, with a focus on Cilium CNI, load balancing, and edge computing patterns.
Networking Overview
RKE2 networking is built around several key components:
- Cilium CNI: eBPF-powered networking replacing traditional kube-proxy
- Layer 4 Load Balancing: High-availability traffic distribution
- Overlay Networks: Secure inter-node communication
- Edge Integration: VPN overlay for remote access
Cilium CNI Configuration
Why Cilium for RKE2
Cilium provides significant advantages over traditional CNI solutions:
- eBPF Performance: Native kernel integration for maximum throughput
- kube-proxy Replacement: Eliminates IPTABLES overhead
- Advanced Observability: Deep packet inspection via Hubble
- Service Mesh Features: L7 policies without sidecars
- Security: Network policies with microsegmentation
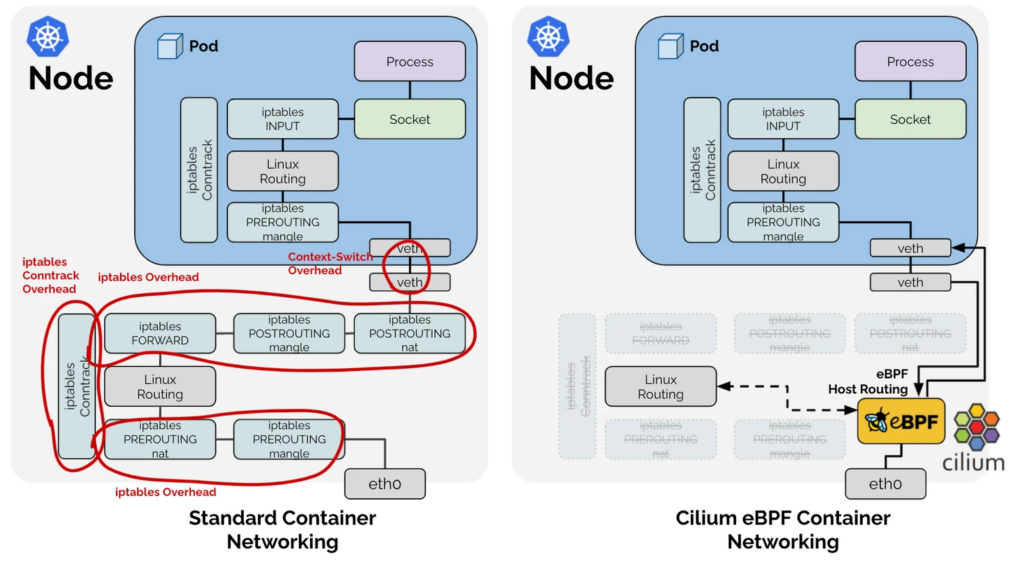
Cilium replaces kube-proxy with eBPF for superior performance
Production Cilium Configuration
RKE2 uses HelmChartConfig to customize Cilium. Create the following configuration:
# /var/lib/rancher/rke2/server/manifests/rke2-cilium-config.yaml
apiVersion: helm.cattle.io/v1
kind: HelmChartConfig
metadata:
name: rke2-cilium
namespace: kube-system
spec:
valuesContent: |-
# Replace kube-proxy entirely
kubeProxyReplacement: true
# API server configuration
k8sServiceHost: "localhost"
k8sServicePort: "6443"
# Enable Hubble observability
hubble:
enabled: true
relay:
enabled: true
ui:
enabled: true
# Optional: Enable eBPF optimizations for production
bpf:
masquerade: true
hostServices:
enabled: true
datapathMode: "netkit" # Use netkit for better performance
# Optional: Enable WireGuard encryption
encryption:
enabled: true
type: "wireguard"
# Operator configuration
operator:
replicas: 1 # Use 2+ for HA deploymentsBasic Configuration (Edge Deployments)
For edge environments with resource constraints, use this minimal configuration:
# /var/lib/rancher/rke2/server/manifests/rke2-cilium-config.yaml
apiVersion: helm.cattle.io/v1
kind: HelmChartConfig
metadata:
name: rke2-cilium
namespace: kube-system
spec:
valuesContent: |-
kubeProxyReplacement: true
k8sServiceHost: "localhost"
k8sServicePort: "6443"
hubble:
enabled: true
relay:
enabled: true
ui:
enabled: true
operator:
replicas: 1Verifying Cilium Installation
# Check Cilium status
cilium status
# Verify connectivity
cilium connectivity test
# Check Hubble
hubble statusLoad Balancer Configuration
High Availability Requirements
For production RKE2 clusters, implement Layer 4 TCP load balancing to ensure high availability:
- Minimum 2 Load Balancers: Active-passive configuration
- Odd Number of Servers: 3+ server nodes for etcd quorum
- Health Checks: Monitor backend server health
- Session Persistence: Not required for Kubernetes API
NGINX Load Balancer Setup
Installation
# Install NGINX
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y nginx
# Create nginx service user
sudo adduser --system --no-create-home --shell /bin/false --disabled-login --group nginx
# Enable service
sudo systemctl enable nginx
sudo systemctl start nginxConfiguration
# /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
worker_rlimit_nofile 40000;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 8192;
use epoll;
multi_accept on;
}
stream {
# RKE2 Supervisor API (9345)
upstream rke2_supervisor {
least_conn;
server 192.168.10.10:9345 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=5s;
server 192.168.10.11:9345 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=5s;
server 192.168.10.12:9345 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=5s;
}
server {
listen 9345;
proxy_pass rke2_supervisor;
proxy_timeout 10s;
proxy_connect_timeout 5s;
}
# Kubernetes API (6443)
upstream kubernetes_api {
least_conn;
server 192.168.10.10:6443 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=5s;
server 192.168.10.11:6443 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=5s;
server 192.168.10.12:6443 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=5s;
}
server {
listen 6443;
proxy_pass kubernetes_api;
proxy_timeout 30s;
proxy_connect_timeout 5s;
}
# HTTP Ingress (80)
upstream ingress_http {
least_conn;
server 192.168.10.13:80 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=5s;
server 192.168.10.14:80 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=5s;
server 192.168.10.15:80 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=5s;
}
server {
listen 80;
proxy_pass ingress_http;
}
# HTTPS Ingress (443)
upstream ingress_https {
least_conn;
server 192.168.10.13:443 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=5s;
server 192.168.10.14:443 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=5s;
server 192.168.10.15:443 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=5s;
}
server {
listen 443;
proxy_pass ingress_https;
}
}HAProxy Alternative (Recommended)
For production environments, HAProxy provides better load balancing features:
# /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
global
daemon
maxconn 4096
defaults
mode tcp
timeout connect 5000ms
timeout client 50000ms
timeout server 50000ms
# RKE2 Supervisor API
frontend rke2_supervisor_frontend
bind *:9345
default_backend rke2_supervisor_backend
backend rke2_supervisor_backend
balance roundrobin
option tcp-check
server server1 192.168.10.10:9345 check
server server2 192.168.10.11:9345 check
server server3 192.168.10.12:9345 check
# Kubernetes API
frontend kubernetes_api_frontend
bind *:6443
default_backend kubernetes_api_backend
backend kubernetes_api_backend
balance roundrobin
option httpchk GET /healthz
server server1 192.168.10.10:6443 check check-ssl verify none
server server2 192.168.10.11:6443 check check-ssl verify none
server server3 192.168.10.12:6443 check check-ssl verify noneFirewall Configuration
Port Requirements Overview
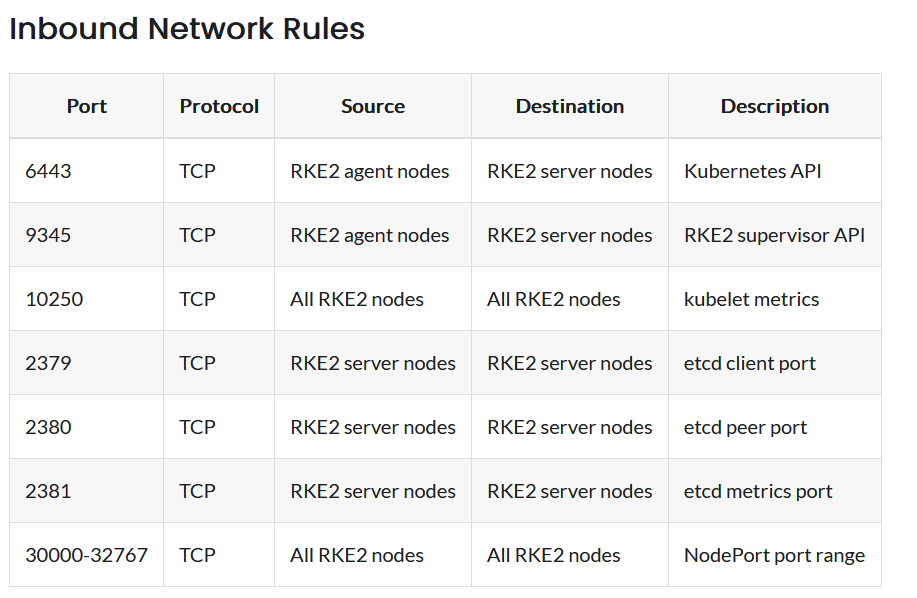
The following ports need to be open in the firewall for RKE2 to work properly:
Cilium CNI Specific Ports
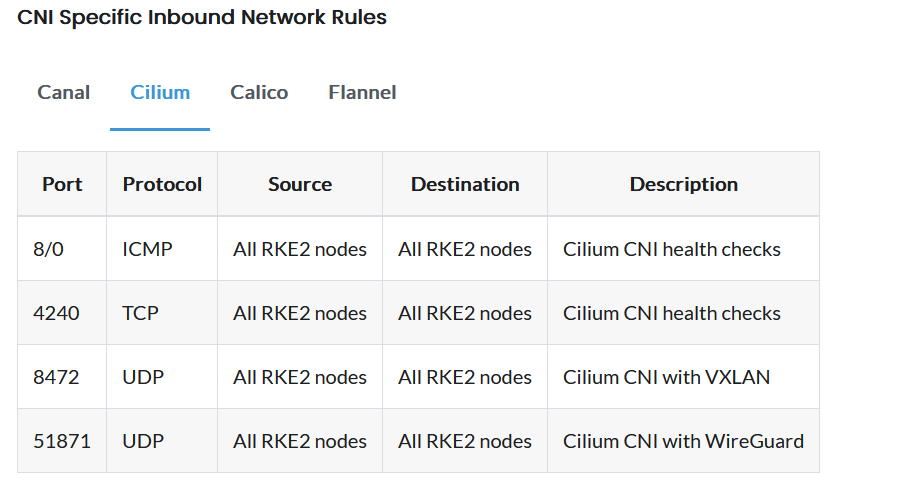
UFW Configuration
Configure UFW for RKE2 networking requirements:
# Server nodes firewall rules
configure_ufw_rke2_server() {
sudo ufw allow 22/tcp # SSH
sudo ufw allow 6443/tcp # Kubernetes API
sudo ufw allow 9345/tcp # RKE2 supervisor
sudo ufw allow 10250/tcp # Kubelet API
sudo ufw allow 2379/tcp # etcd client
sudo ufw allow 2380/tcp # etcd peer
sudo ufw allow 2381/tcp # etcd metrics
sudo ufw allow 4240/tcp # Cilium health
sudo ufw allow 4244/tcp # Hubble gRPC
sudo ufw allow 4245/tcp # Hubble relay
sudo ufw allow 8472/udp # VXLAN
sudo ufw allow 51871/udp # WireGuard
sudo ufw allow 30000:32767/tcp # NodePort range
}
# Agent nodes firewall rules
configure_ufw_rke2_agent() {
sudo ufw allow 22/tcp # SSH
sudo ufw allow 10250/tcp # Kubelet API
sudo ufw allow 4240/tcp # Cilium health
sudo ufw allow 4244/tcp # Hubble gRPC
sudo ufw allow 8472/udp # VXLAN
sudo ufw allow 51871/udp # WireGuard
sudo ufw allow 30000:32767/tcp # NodePort range
}IPTables Rules
For systems not using UFW:
# Server nodes
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 6443 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 9345 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 10250 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 2379:2381 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 4240 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 4244:4245 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 8472 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 51871 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 30000:32767 -j ACCEPT
# Save rules
iptables-save > /etc/iptables/rules.v4Edge Computing Networking
Tailscale Integration
For edge deployments, integrate Tailscale for secure remote access:
Node Configuration with Tailscale
# /etc/rancher/rke2/config.yaml
node-ip: 192.168.10.10 # Internal LAN IP
node-external-ip: 100.64.1.10 # Tailscale overlay IP
tls-san:
- "192.168.10.10" # Internal access
- "100.64.1.10" # Tailscale access
- "node1.tail12345.ts.net" # Tailscale hostname
- "lb.edge.example.com" # Load balancer FQDNTailscale Operator Deployment
Deploy the Tailscale operator for Kubernetes services:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: tailscale-operator
namespace: tailscale
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: tailscale-operator
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: tailscale-operator
spec:
containers:
- name: tailscale
image: tailscale/tailscale:latest
env:
- name: TS_KUBE_SECRET
value: "tailscale-auth"
- name: TS_USERSPACE
value: "false"
securityContext:
capabilities:
add:
- NET_ADMINBandwidth Optimization
For edge environments with limited bandwidth:
# Cilium bandwidth optimization
apiVersion: helm.cattle.io/v1
kind: HelmChartConfig
metadata:
name: rke2-cilium
namespace: kube-system
spec:
valuesContent: |-
# Enable bandwidth management
bandwidthManager:
enabled: true
bbr: true
# Optimize for low bandwidth
tunnel: "disabled" # Use native routing when possible
autoDirectNodeRoutes: true
# Reduce resource usage
operator:
resources:
limits:
cpu: 100m
memory: 128MiNetwork Policies
Cilium Network Policies
Implement microsegmentation with Cilium policies:
apiVersion: cilium.io/v2
kind: CiliumNetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: edge-cluster-isolation
namespace: production
spec:
endpointSelector:
matchLabels:
env: production
ingress:
- fromEndpoints:
- matchLabels:
env: production
- fromEndpoints:
- matchLabels:
k8s:io.kubernetes.pod.namespace: kube-system
egress:
- toEndpoints:
- matchLabels:
env: production
- toFQDNs:
- matchName: "api.edge.example.com"Monitoring and Observability
Hubble Configuration
Enable comprehensive network observability:
# Install Hubble CLI
HUBBLE_VERSION=$(curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/hubble/master/stable.txt)
curl -L --remote-name-all https://github.com/cilium/hubble/releases/download/$HUBBLE_VERSION/hubble-linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar xf hubble-linux-amd64.tar.gz
sudo mv hubble /usr/local/binNetwork Flow Monitoring
# Monitor network flows
hubble observe
# Filter by namespace
hubble observe --namespace kube-system
# Monitor dropped packets
hubble observe --verdict DROPPED
# Export flows to JSON
hubble observe -o json > network-flows.jsonTroubleshooting
Common Networking Issues
# Check Cilium status
cilium status
# Verify node connectivity
cilium node list
# Test policy enforcement
cilium policy get
# Debug DNS resolution
cilium connectivity test --test dns-only
# Check load balancer health
curl -k https://lb.edge.example.com:6443/healthzThis networking configuration provides a robust, secure, and observable foundation for production RKE2 deployments with edge computing capabilities.
